Adsorption-Desorption of Cd(II) and Mg(II) Ions by Dithizone-Immobilized Coal Bottom Ash
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55749/ijcs.v4i2.76Keywords:
Adsorption-desorption, Cd(II), Coal bottom ash, Dithizone, Mg(II)Abstract
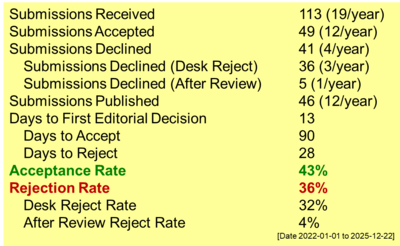
Dithizone-immobilized coal bottom ash (DICBA) was successfully prepared as Cd(II) and Mg(II) adsorbent. The parameters examined in the metal ion adsorption study included the effect of pH, adsorbent mass, contact time, and initial concentration. Sequential desorption was examined using H2O, KNO3, HNO3, and Na2EDTA. The results showed that dithizone had been successfully immobilized on the activated coal bottom ash, as verified by FTIR spectroscopy and XRD analyses. Specific wavenumbers observed included the aromatic group C=C at 1496 cm-1, the C-N group at 1319 cm-1 and the Si-O-Si at 1087 cm-1 with d-spacing values of 8.313 and 6.046 Å. The optimum conditions for adsorption were 60 min for Cd(II) and 90 min for Mg(II) at a pH of 5 with 0.2 g of adsorbent mass, and an initial concentration of Cd(II) at 50 ppm. The adsorption kinetics of Cd(II) and Mg(II) followed the Ho pseudo-second-order model with 0.174 and 0.285 (g/mol·min) rate constants for Cd(II) and Mg(II), respectively. The highest correlation coefficients (R2) were 0.995 for Cd(II) and 0.999 for Mg(II). Isotherm modeling indicated that the adsorption of Cd(II) best fitted the Langmuir model (R² = 0.988), followed by the Dubinin–Radushkevich (R² = 0.952), Freundlich (R² = 0.843), and Temkin (R² = 0.827) models. The desorption mechanism for Cd(II) and Mg(II) was formed by various interactions, such as physical mechanism (28.25% and 26.26%), ion exchange (23.13% and 14.15%), hydrogen bond formation (16.90% and 12.11%), and the mechanism of complex formation (9.56% and 6.13%).
References
[1] Vajargah, M.F. 2021. A review on the effects of heavy metals on aquatic animals. J. Biomed. Res. Environ. Sci. 2(9). 865-869. http://dx.doi.org/10.37871/jbres1324
[2] Jais, N., Ikhtiar, M., Gafur, A., & Abbas, H.H., 2020. Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals Cadmium (Cd) and Chromium (Cr) Found in Water and Fish in the Tallo River Makassar. Window of Public Health Journal. 1(3). 261–273. https://doi.org/10.33096/woph.v1i3.65
[3] Cordova, M.R. 2021. A preliminary study on heavy metal pollutants chrome (Cr), cadmium (Cd), and lead (Pb) in sediments and beach morning glory vegetation (ipomoea pes-caprae) from dasun estuary, Rembang, Indonesia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 162. 111819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111819
[4] World Health Organization (WHO). 2017. Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality: Fourth Edition Incorporating the First Addendum. Geneva: World Health Organization.
[5] Huda, B.N., Wahyuni, E.T., Mudasir, M., 2021. Eco-friendly immobilization of dithizone on coal bottom ash for the adsorption of lead(II) ion from water. Results Eng. 10. 100221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rineng.2021.100221
[6] Mudasir, M., Karelius, K., Aprilita, N.H., Wahyuni, E.T. 2016. Adsorption of mercury(II) on dithizone-immobilized natural zeolite. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 4. 1839–1849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2016.03.016
[7] Dong, Y., Zhou, M., Xiang, Y., Wan, S., Li, H., & Hou, H. 2019. Barrier effect of coal bottom ash-based geopolymers on soil contaminated by heavy metals. RSC Adv. 9(42). 28695–28703. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra05542h
[8] Fitriana, D., Mudasir, M., Siswanta, D. 2020. Adsorption of Pb(II) from aqueous solutions on dithizone-immobilized coal fly ash. Key Eng. Mater. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/kem.840.57
[9] Basuki, R., Apriliyanto, Y., Stiawan, E., Pradipta, A.R., Rusdiarso, B., & Putra, B.R. 2025. Magnetic hybrid chitin-horse manure humic acid for optimized Cd(II) and Pb(II) adsorption from aquatic environment. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 11. 101138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscee.2025.101138
[10] Huang, J., Yuan, F., Zeng, G., Li, X., Gu, Y., Shi, L., Liu, W., Shi, Y. 2017. Influence of pH on heavy metal speciation and removal from wastewater using micellar-enhanced ultrafiltration. Chemosphere. 173. 199-206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.12.137
[11] Tajudin, W.S., Sunarti, S., & Manuhutu, J. B. (2023). Optimasi Massa Adsorben Dan pH Pada Adsorpsi Ion Fe Menggunakan Abu Cangkang Kelapa Sawit. Molluca Journal of Chemistry Education. 13(2). 74–86. https://doi.org/10.30598/MJoCEvol13iss2pp74-86
[12] Krisdiyanto, D., Khamidinal, & Faqih, A. 2022. Adsorption Cd (II) by Zeolite from Bottom Ash Modified by Dithizone. J. Trop. Chem. Res. Edu. 4(2). 110–125. https://doi.org/10.14421/jtcre.2022.42-06
[13] Basuki, R., Santosa, S.J. and Rusdiarso, B. 2017. Ekstraksi adsorben ramah lingkungan dari matriks biologi: asam humat tinja kuda (AH-TK). Chempublish J. 2(1). 13-25.
[14] Sari, M.K., Basuki, R. and Rusdiarso, B., 2021. Adsorption of Pb(II) from aqueous solutions onto humic acid modified by urea-formaldehyde: Effect of pH, ionic strength, contact time, and initial concentration. Indones. J. Chem. 21(6). 1371-1388. https://doi.org/10.22146/ijc.64600
[15] Ngatijo, N., Gusmaini, N., Bemis, R. and Basuki, R. 2021. Adsorption of methylene blue on humic acid coated magnetite nanoparticles: isotherm and kinetic study. Chemical Engineering Research Articles. 4(1). 51-64. https://doi.org/10.25273/cheesa.v4i1.8433.51-64
[16] Basuki, R., Yusnaidar, Y. and Rusdiarso, B. 2018. Different style of Langmuir isotherm model of non-competitive sorption Zn(II) and Cd(II) onto horse dung humic acid (HD-HA). AIP Conf. Proc. 2026(1). 020009. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5064969
[17] Basuki, R., Santosa, S.J. and Rusdiarso, B. 2017. The novel kinetics expression of Cadmium(II) removal using green adsorbent horse dung humic acid (HD-HA). AIP Conf. Proc. 1823(1). 020001. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4978074
[18] Ngatijo, N., Permana, E., Yanti, L.P., Ishartono, B. and Basuki, R., 2021. Remazol briliant blue uptake by green and low-price black carbon from ilalang weeds (Imperata cylindrica) activated by KOH solution. JKPK (Jurnal Kimia dan Pendidikan Kimia). 6(2). 192-205. https://doi.org/10.20961/jkpk.v6i2.53113
[19] Ngatijo, N., Basuki, R., Nuryono, N. and Rusdiarso, B. 2019. Comparison of Au(III) Sorption on Amine-Modified Silica (AMS) and Quaternary Amine-Modified Silica (QAMS): A Thermodynamic and Kinetics Study. Indones. J. Chem. 19(2). 337-346. https://doi.org/10.22146/ijc.33758
[20] Basuki, R., Rusdiarso, B., Santosa, S.J., Siswanta, D. 2021. The dependency of kinetic parameters as a function of initial solute concentration: New insight from adsorption of dye and heavy metals onto humic-like modified adsorbents. Bull. Chem. React. Eng. Catal. 16(4). 773-795. https://doi.org/10.9767/bcrec.16.4.11816.773-795
[21] Yahya, M.D., Abubakar, H., Obayomi, K.S., Iyaka, Y.A., & Suleiman, B. 2020. Simultaneous and continuous biosorption of Cr and Cu (II) ions from industrial tannery effluent using almond shell in a fixed bed column. Results Eng. 6. 100113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. rineng.2020.10011
[22] Irawan, C., Dahlan, B., & Retno, N. 2021. The effect of adsorbent mass, contact time and adsorbent activation using hcl on the effectiveness of heavy metal (fe) reduction using fly ash as an adsorbent. Jurnal Teknologi Terpadu. 3(2). 89–96. https://doi.org/10.32487/jtt.v3i2.89
[23] Haryanto, B., Sinaga, W.K., & Saragih, F.T. 2019. Study of interaction model on adsorption of heavy metal cadmium (Cd²⁺) using black sand adsorbent. Jurnal Teknik Kimia USU. 8(2). 79-84. https://doi.org/10.32734/jtk.v8i2.2032
[24] Shi, Q., Terracciano, A., Zhao, Y., Wei, C., Christodoulatos, C., Meng, X. 2019. Evaluation of metal oxides and activated carbon for lead removal: kinetics, isotherms, column tests, and the role of co-existing ions. Sci. Total Environ. 648. 176–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.013
[25] Rahayu, I., Nazriati, Fajaroh, F. & Nur, A. 2019. Cadmium Ion Adsorption Using Bagasse-Based Silica Xerogel. Journal Cis-Trans. 3(1). 10-16. http://dx.doi.org/10.17977/um0260v3i12019p010
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Indonesian Journal of Chemical Studies

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.