A Technical Study on the Effect of Hydrothermal and Dry Heat Shrinkage of Different Shoe-Upper Leathers Used in Pakistan
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55749/ijcs.v2i1.10Keywords:
Leather shoe, Physical testing, ShrinkageAbstract
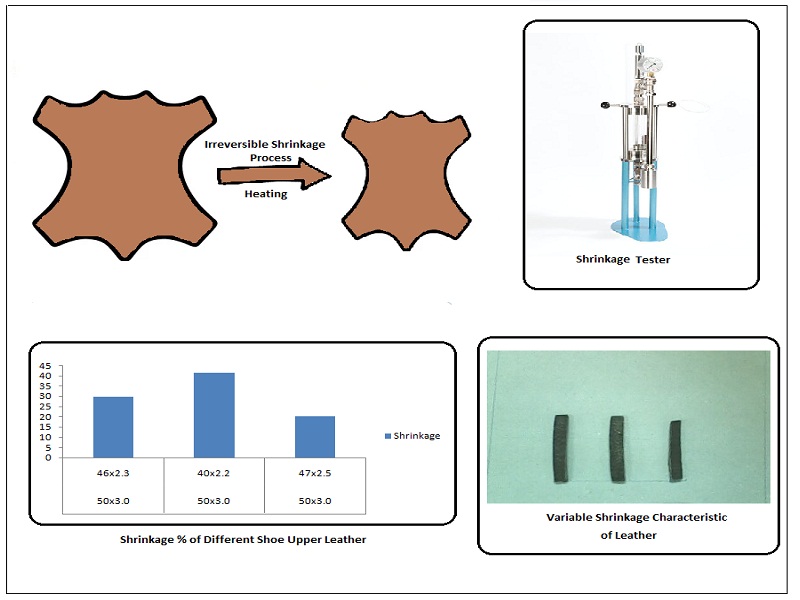
The shrinkage of leather becomes a problem when leather is used in the form of leather shoes or other products and is heated at a high temperature. This technical study addressed shrinkage occurring in most leather shoes used in Pakistan during the shoe manufacturing process. The chemical testing results revealed fat content (4.0-4.5%), chromic oxide (2.3-2.5%), ash content (1.3-1.6%), and pH (3.5-3.7) under significant limits. The effects of hydrothermal and dry heat shrinkage were investigated in selected shoe-upper leathers. The leather samples showed (18-41%) shrinkage in all 03 samples. The results revealed that an extensive change in various physical tests, such as tensile strength, % elongation, tear strength, had been found with heat induction. The temperature and time of heat contact significantly affect the destruction of bonding in shoe upper leather after being converted into shoes.
References
Tang, K., Liu, J., Wang, F., & Cao, J. 2003. Dry heat resistance of hide and leather. J. Am. Leather Chem. Assoc. 98(5). 168-172.
Abebe, G. and Schaefer, F. 2014. High Hopes and Limited Successes: Experimenting with Industrial Polices in the Leather Industry in Ethiopia. EDRI Working Paper 011. Addis Ababa: Ethiopian Development Research Institute. p. 43.
Leather research section of Northwest Institute of Light Industry. 1996. Leather Analysis. Beijing: Light Industry Press, China.
Bitlisli B.O., Karavana H.A., Başaran B., & Aslan A. 2005. Importance of using genuine leather in shoe production in terms of foot comfort. J. Soc. Leather Technol. Chem. 89(3). 107-110.
Bitlisli, B., Adıgüzel, Z. A., Yeldiyar, G., Kairanbekov, G., & Küçükakın, E. 2013. Upper leathers in shoe manufacturing. J. Ind. Technol. Eng. 2(07). 37-41.
Sharphouse J.H. 1995. Leather Technician's Handbook 2nd Edition. Northampton: Leather Producer's Association, England.
Miles, C.A., Avery, N.C., Rodin, V.V., & Bailey, A.J. 2005. The increase in denaturation temperature following cross-linking of collagen is caused by dehydration of the fibres. J. Mol. Biol. 346(2). 551-556. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.12.001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2004.12.001
Valeika, V., Širvaitytė, J., & Beleška, K. 2010. Estimation of chrome-free tanning method suitability in conformity with physical and chemical properties of leather. Mater. Sci-Medzg. 16(4). 330-336.
Morera, J.M., Esteban, B., Baquero, G., & Cuadros, R. 2019. A new system to measure leather shrinkage temperature. XXXV IULTCS Congress Dresden proceeding. 8th Freiberg Leather Days. Dresden, 25-28 June 2019.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Indonesian Journal of Chemical Studies

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.