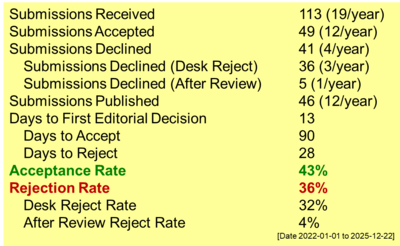
Reaction Mechanism in Standardized α-Cellulose Content Test: Study from Boehmeria nivea Fiber
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55749/ijcs.v3i1.45Abstract
In defense industry, α-cellulose is the main component of nitrocellulose propellant. However, a detailed description of the reaction mechanism of each treatment step in SNI 0444-2009 is still very scarce. This study addresses this gap by presenting the reaction mechanisms of each treatment and the symbols used in the SNI 0444-2009 procedure. The separation of lignin from α-cellulose occurred by breaking the C‒O bond linking them. This bond was broken by the ‒OH group of NaOH via a hydrolysis reaction. The reaction was initiated with the elimination of a hydrogen atom from the lignin structure by the hydroxyl ion (‒OH), and the C‒O bond was broken by a hydrolysis reaction. The breaking of this bond was indicated by the disappearance of the IR peaks at wavenumbers 1049 and 1190 cm–1 in the filtrate after extraction. The SNI 0444-2009 method for the α-cellulose content test was carried out by a redox back titration of Cr(VI) with Fe(II) from ferrous ammonium sulfate. This titration was conducted to calculate the amount of Cr(VI) ions in potassium dichromate or Cr(VI) that did not react with lignin or beta cellulose in the filtrate. Understanding the contribution and reaction mechanisms of each compound involved in the SNI 0444-2009 procedure contributed to obtaining accurate data on α-cellulose content. In this study, the calculated α-cellulose content of the flax fiber was 96.75%. Furthermore, the detailed mechanism of the redox reaction was discussed in detail in this paper.
References
Fleming, J., Rousseau, W., Zebregs, M., van Driel, C. 2022. Solventless extruded double-base (EDB) propellant chargesâ a review of the properties, technology, and applications. Int. J. Energetic Mater. Chem. Propul. 21(3). 13-46. doi: https://doi.org/10.1615/IntJEnergeticMaterialsChemProp.v21.i3.20.
Geng, W., Narron, R., Jiang, X., Pawlak, J.J., Chang, H.M., Park, S., Jameel, H., Venditti, R.A. 2019. The influence of lignin content and structure on hemicellulose alkaline extraction for non-wood and hardwood lignocellulosic biomass. Cellulose. 26. 3219-3230. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02261-y.
Li, X. 2021. Plant cell wall chemistry: Implications for ruminant utilisation. J. Appl. Anim. Nutr. 9(1). 31-56. doi: https://doi.org/10.3920/JAAN2020.0017.
Sangalang, R.H. 2021. Kapok fiber-structure, characteristics and applications: a review. Orient. J. Chem. 37(3). 513-523. doi: https://doi.org/10.13005/ojc/370301.
Siakeng, R., Jawaid, M., Tahir, P.M., Siengchin, S., Asim, M. 2020. Improving the Properties of Pineapple Leaf Fibres by Chemical Treatments. In: Jawaid, M., Asim, M., Tahir, P., Nasir, M. (eds) Pineapple Leaf Fibers. Green Energy and Technology. 55-71. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-1416-6_4.
Manian, A.P., Cordin, M., Pham, T. 2021. Extraction of cellulose fibers from flax and hemp: a review. Cellulose 28(13). 8275-8294. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04051-x.
Mishra, L., & Basu, G. 2020. Coconut fibre: its structure, properties and applications. In Handbook of natural fibres (pp. 231-255). Woodhead Publishing.
Abd El-Sayed, E.S., El-Sakhawy, M., El-Sakhawy, M.A.M. 2020. Non-wood fibers as raw material for pulp and paper industry. Nord. Pulp Pap. Res. J. 35(2). 215-230. doi: https://doi.org/10.1515/npprj-2019-0064.
Ikhtiarini, N., Masruri, M., & Ulfa, S.M. 2022. Synthesis and characterization of cellulose acetate and nanocellulose acetate from sengon agroindustrial waste (Paraserianthes falcataria). J. Pure Appl. Chem. Res. 11(3). 214-224. doi: https://doi.org/10.21776/ub.jpacr.2022.011.03.644.
Rana, V., Malik, S., Joshi, G., Rajput, N.K., Gupta, P.K. 2021. Preparation of alpha cellulose from sugarcane bagasse and its cationization: Synthesis, characterization, validation and application as wet-end additive. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 170. 793-809. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.12.165.
Basuki, R., Yusnaidar, Y., Rusdiarso, B. 2018. Different style of Langmuir isotherm model of non-competitive sorption Zn(II) and Cd(II) onto horse dung humic acid (HD-HA), AIP Conf. Proc. 2026(1). 1-13. doi: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5064969.
Bolilanga, P.I.W., Sekarini, A., Toharani, D.C., Rahmawati, F., Basuki, R., Ishartono, B., Fahri, M. 2022. Physical strength improvement of nata de coco by water replacement with carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) as a potential bulletproof material: a preliminary study. Indones. J. Chem. Stud. 1(2). 54-58. doi: https://doi.org/10.55749/ijcs.v1i2.19.
Ngatijo, N., Basuki, R., Nuryono, N., Rusdiarso, B. 2019. Comparison of Au(III) Sorption on amine-modified silica (AMS) and quaternary amine-modified silica (QAMS): A thermodynamic and kinetics study. Indones. J. Chem. 19(2). 337-346. doi: https://doi.org/10.22146/ijc.33758.
Paramitha, T., & Sitompul J.P. 2020. Characterization of biocomposites from polylactic acid and cellulose of oil palm empty fruit bunch. J. Kim. Pendidik. Kim. 5(3). 275-281. doi: https://doi.org/10.20961/jkpk.v5i3.39212.
Zhang, T., Yan, S., Hao, J., Li, D. 2021. Experimental and theoretical investigations of terahertz spectra of the structural isomers: Mannose and galactose. J. Spectrosc. 469262. 1-9. doi: https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/3469262.
Jiang, B., Shen, F., Jiang, Y., Huang, M., Zhao, L., Lei, Y., Shen, F. 2024. Extraction of super high-yield lignin-carbohydrate complexes from rice straw without compromising cellulose hydrolysis. Carbohydr. Polym. 323. 121452. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.121452.
Zhou, H., Xu, J.Y., Fu, Y., Zhang, H., Yuan, Z., Qin, M., Wang, Z. 2019. Rapid flow-through fractionation of biomass to preserve labile aryl ether bonds in native lignin. Green Chem. 21. 4625-4632. doi: https://doi.org/10.1039/C9GC02315A.
Ng, C.Y., Khoo, L.H., Ng, L.Y., Ong, C.B., Mahmoudi, E., Rohani, R., & Mohammad, A.W. 2020. Novel polyethersulfone-cellulose composite thin film using sustainable empty fruit bunches from Elaeis guineensis for methylene blue removal. Polym. Test. 86. 106494. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2020.106494.
Prieto-García, F., Jiménez-Muñoz, E., Acevedo-Sandoval, O. A., Rodríguez-Laguna, R., Canales-Flores, R. A., & Prieto-Méndez, J. 2019. Obtaining and optimization of cellulose pulp from leaves of Agave tequilana Weber Var. Blue. Preparation of handmade craft paper. Waste and Biomass Valori. 10. 2379-2395. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0262-5.
Mongioví, C., Morin-Crini, N., Lacalamita, D., Bradu, C., Raschetti, M., Placet, V., Riberio, A.R.L., Ivanovska, A., Kostic, M., Crini, G. 2021. Biosorbents from plant fibers of hemp and flax for metal removal: Comparison of their biosorption properties. Molecules, 26(14). 4199. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26144199.
Kopania, E., Wietecha, J., & Ciechańska, D. 2012. Studies on isolation of cellulose fibres from waste plant biomass. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 20(6B(96)). 167-172.
Lazić, B.D., Pejić, B.M., Kramar, A.D., Vukčević, M.M., Mihajlovski, K.R., Rusmirović, J.D., & Kostić, M.M. 2018. Influence of hemicelluloses and lignin content on structure and sorption properties of flax fibers (Linum usitatissimum L.). Cellulose. 25. 697-709. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1575-4.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Indonesian Journal of Chemical Studies

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.