Synthesis and Characterization of Titanium Dioxide/Graphene Nanoplatelets Nanocomposites via Planetary Ball Milling for Military Radar Absorbing Materials
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55749/ijcs.v4i1.67Keywords:
Graphene nanoplatelets, Nanocomposites, Planetary ball milling, Radar absorbing material, Titanium dioxideAbstract
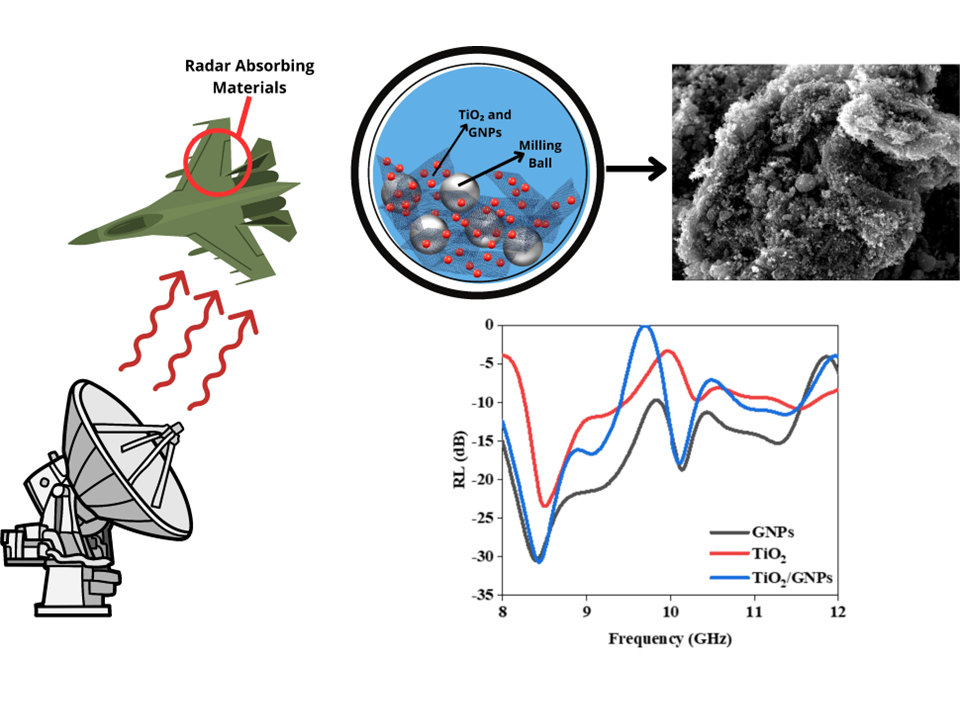
Stealth technology is widely used in the military field to avoid enemy detection. Consequently, there has been a significant surge in research related to radar-absorbing materials (RAMs). Titanium dioxide (TiO2) and graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs) are promising materials for developing RAMs. Combining TiO2 as a semiconductor with GNPs as a conductive material could increase the ability to absorb microwaves through a more effective energy dissipation mechanism. In our study, TiO2 and GNPs were fabricated using the planetary ball milling method. The structure and morphology of the resulting nanocomposites were evaluated using Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy with Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy with Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (FE-SEM EDS) and X-ray Diffraction (XRD). FE-SEM observations showed that TiO2 nanoparticles were attached to the surface of layered GNPs. XRD analysis showed a decrease in the peak intensity of the TiO2/GNP nanocomposites compared to pure TiO2 due to the addition of carbon elements. The performance of RAMs was evaluated using a Vector Network Analyzer (VNA) in the X-band (8-12 GHz) range with a 3-mm thickness. The VNA analysis indicated that the TiO2/GNP nanocomposites exhibited the optimal reflection loss (RL) of -30.72 dB at a frequency of 8.42 GHz, accompanied by a through power of 99.91%. Consequently, TiO2/GNP nanocomposites demonstrated promising potential as a military RAM.
References
Ivan Z.J.J. & Kim, Y. 2003. Synthetic Aperture Radar. In: Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology. Elsevier. pp 451–465.
Qu, S., Wu, G., Fang, J., Zang, D., Xing, H., Wang, L., & Wu, H. 2017. Dielectric and magnetic loss behavior of nanooxides. In Spectroscopic Methods for Nanomaterials Characterization. 301-319. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-46140-5.00011-X.
Nag, A., Simorangkir, R.B., Gawade, D.R., Nuthalapati, S., Buckley, J.L., O'Flynn, B., Altinsoy, M.E., & Mukhopadhyay, S.C. 2022. Graphene-based wearable temperature sensors: A review. Mater. Des. 221. 110971. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2022.110971.
Wang, L., Aslani, F. 2019. A review on material design, performance, and practical application of electrically conductive cementitious composites. Constr. Build Mater. 229. 116892. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.116892.
Sathish, K.M., Joseph, A., James, R.K.C., Jayavel, R. 2025 Engineering multifunctionality graphene-based nanocomposites with epoxy-silane functionalized cardanol for next-generation microwave absorber. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 678. 407–420. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2024.08.193.
Silva, A.A., Stein, R., Campos, D., Indrusiak, T., Soares, B.G., & Barra, G.M. 2019. Conducting materials based on epoxy/graphene nanoplatelet composites with microwave absorbing properties: effect of the processing conditions and ionic liquid. Front. Mater. 6. 156. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmats.2019.00156.
Qiao, J., Zhang, X., Xu, D., Kong, L., Lv, L., Yang, F., Wang, F., Liu, W., & Liu, J. 2020. Design and synthesis of TiO2/Co/carbon nanofibers with tunable and efficient electromagnetic absorption. Chem. Eng. J. 380. 122591. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.122591.
Yang, Z., Luo, F., Hu, Y., Duan, S., Zhu, D., & Zhou, W. 2016. Dielectric and microwave absorption properties of TiO2/Al2O3 coatings and improved microwave absorption by FSS incorporation. J. Alloys Compd. 678. 527–532. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.04.031.
Xia, T., Zhang, C., Oyler, N.A., & Chen, X. 2013. Hydrogenated TiO2 nanocrystals: a novel microwave absorbing material. Adv. Mater. 25(47). 6905-6910. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201303088.
Zhang, H., Zhao, Y., Yang, X., Zhao, G., Zhang, D., Huang, H., Yang, S., Wen, N., Javid, M., Fan, Z. & Pan, L. 2020. A facile synthesis of novel amorphous TiO2 nanorods decorated rGO hybrid composites with wide band microwave absorption. Nanomaterials. 10(11). 2141. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112141.
Xu, J., Qi, X., Luo, C., Qiao, J., Xie, R., Sun, Y., Zhong, W., Fu, Q. & Pan, C. 2017. Synthesis and enhanced microwave absorption properties: a strongly hydrogenated TiO2 nanomaterial. Nanotechnology. 28(42). 425701. doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6528/aa81ba.
Mo, Z., Yang, R., Lu, D., Yang, L., Hu, Q., Li, H., Zhu, H., Tang, Z. & Gui, X. 2019. Lightweight, three-dimensional carbon Nanotube@ TiO2 sponge with enhanced microwave absorption performance. Carbon. 144. 433-439. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2018.12.064.
Park, S.J. & Seo, M.K., 2011. Solid-solid interfaces. Interface science and technology. 18. 253-331. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-375049-5.00004-9.
Zheng, H., Zhang, W., Li, B., Zhu, J., Wang, C., Song, G., Wu, G., Yang, X., Huang, Y. & Ma, L. 2022. Recent advances of interphases in carbon fiber-reinforced polymer composites: A review. Compos. B. Eng. 233. 109639. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2022.109639.
Liu, X. and Fu, J. 2020. Electronic and elastic properties of the tetragonal anatase TiO2 structure from first principle calculation. Optik. 206. 164342. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.164342.
Li, C., Dang, S., Zhang, C., Wang, L. & Han, P. 2014. Effects of native defects on the electronic structure and photocatalytic activity in anatase TiO2 by first principles calculations. Optik. 125(13). 3145-3149. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2013.12.010.
Fleck, N., Amli, H., Dhanak, V. & Ahmed, W. 2021. Characterization techniques in energy generation and storage. In Emerging Nanotechnologies for Renewable Energy. 259-285. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-821346-9.00003-1.
Latif, Z., Rehman, A.U., Amin, N., Arshad, M.I. & Marzouki, R. 2023. Graphene nanoplatelets (GNPs): a source to bring change in the properties of Co–Ni–Gd-ferrite/GNP nanocomposites. RSC Adv. 13(49). 34308-34321. doi: https://doi.org/10.1039/D3RA02080K.
Saravanan, S. & Dubey, R.S. 2021. Optical and morphological studies of TiO2 nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel method. Mater. Today Proc. 47. 1811-1814. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.03.207.
Zhang, H., Krooswyk, S. & Ou, J. 2015. High speed digital design: design of high speed interconnects and signaling. Elsevier. 199–219.
Elmahaishi, M.F., Azis, R.A.S., Ismail, I. & Muhammad, F.D., 2022. A review on electromagnetic microwave absorption properties: their materials and performance. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 20. 2188-2220. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.07.140.
Wang, G., Li, C., Estevez, D., Xu, P., Peng, M., Wei, H. & Qin, F. 2023. Boosting interfacial polarization through heterointerface engineering in MXene/graphene intercalated-based microspheres for electromagnetic wave absorption. Nanomicro. Lett. 15(1). 152. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-023-01123-4.
Li, C., Deng, L., He, J., Peng, S., Huang, S. & Qiu, L. 2023. Multi-interfacial TiO2/carbon fibers encapsulated with needle-like FeCo2O4 for excellent microwave absorption. Appl. Surf. Sci. 629. 157417. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2023.157417.
Tao, E., Ma, Z., Yang, S., Li, Y., Ma, D., Xing, Z. & Li, Y. 2020. Enhanced electrical conductivity of TiO2/graphene: The role of introducing Ca2+. J. Alloys Compd. 827. 154280. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154280.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Indonesian Journal of Chemical Studies

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.