Study of Anaerobic and Aerobic Fertilizers of Organic Waste Treatment
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55749/ijcs.v3i2.48Keywords:
Aerobic, Anaerobic, Compost, Organic waste fertilizers, PhosporusAbstract
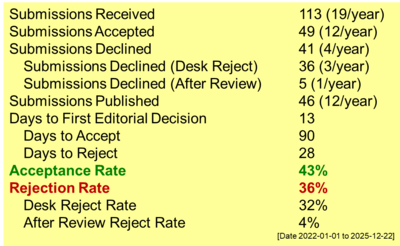
Phosphorus is a critical nutrient for plant growth, significantly enhancing agricultural productivity and ecosystem sustainability. Organic waste-based fertilizers offer a sustainable solution to boost soil phosphorus levels while addressing waste management challenges. This study evaluated the phosphorus content of anaerobic and aerobic fertilizers derived from organic waste, focusing on factors that influence phosphorus dynamics during composting. Composting methods and feedstock composition affected phosphorus transformation and availability, with temperature, moisture, aeration, and microbial activity playing pivotal roles in mineralization, immobilization, and solubilization. The experiment used market waste, pineapple peel, dry leaves, sawdust, water, sugar, manure, and EM4. The composting process involved weekly monitoring of pH, temperature, and compost height. The results showed that the pH of the anaerobic compost ranged from 7.2 to 7.4, meeting the SNI 19-7030-2004 standard. The mature compost color was brownish-black, which also complied with the standard. Phosphorus contents as P2O5 were 1712 mg/kg in aerobic fertilizer and 2653 mg/kg in anaerobic fertilizer. Phosphorus is crucial for root development, water, and nutrient absorption, and enhances plant tolerance to drought. It also affects flower and fruit formation, affecting crop yield quality and quantity. This study highlighted the importance of understanding phosphorus dynamics to optimize nutrient management and improve organic waste utilization in agriculture. Future research should explore the phosphorus transformation mechanisms and innovative composting techniques to enhance phosphorus availability for plant uptake
References
Slorach P.C., Jeswani, H.K., Cuéllar-Franca R. & Azapagic, A. 2019. Environmental and economic implications of recovering resources from food waste in a circular economy. Sci. Total Environ. 693. 133516. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.322.
Slorach P.C., Jeswani H.K., Cuéllar-Franca R. & Azapagic A. 2019. Environmental sustainability of anaerobic digestion of household food waste. J. Environ. Manage. 236. 798-814. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.02.001.
Han F., Yun S., Zhang C., Xu H. & Wang Z. 2019. Steel slag as accelerant in anaerobic digestion for nonhazardous treatment and digestate fertilizer utilization. Bioresour. Technol. 282. 331-338. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.03.029.
Pramanik S.K., Suja F.B., Zain S.M., & Pramanik B.K. 2019. The anaerobic digestion process of biogas production from food waste: Prospects and constraints. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 8. 100310. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biteb.2019.100310.
Satrio G., Hasibuan A.K.H., & Azzida P.W. 2023. Organic fertilizer from amino acid and eco-enzyme combinations for repairing plant metabolism. Indones. J. Chem. Stud. 2(1). 22–26. doi: https://doi.org/10.55749/ ijcs.v2i1.28.
Toor M.D., Adnan M., Rehman F.U., Tahir R., Saeed M.S., Khan A.U. & Pareek V. 2021. Nutrients and their importance in agriculture crop production; A review. Ind. J. Pure App. Biosci. 9(1). 1-6. doi: https://doi.org/10.18782/2582-2845.8527.
Jiang B., Jianlin S.H.E.N., Minghong S.U.N., Yajun H.U., Jiang W., Juan W.A.N.G., Yong L.I. & Jinshui W.U. 2021. Soil phosphorus availability and rice phosphorus uptake in paddy fields under various agronomic practices. Pedosphere. 31(1). 103-115. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(20)60053-4.
Ma Y., & Liu Y. 2019. Turning food waste to energy and resources towards a great environmental and economic sustainability: An innovative integrated biological approach. Biotechnol. Adv. 37(7).107414. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2019.06.013.
Witek-Krowiak A., Gorazda K., Szopa D., Trzaska K., Moustakas K., & Chojnacka K. 2022. Phosphorus recovery from wastewater and bio-based waste: an overview. Bioengineered. 13(5). 13474-13506. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2022.2077894.
Rehman R.A., & Qayyum M.F. 2020. Co-composts of sewage sludge, farm manure and rock phosphate can substitute phosphorus fertilizers in rice-wheat cropping system. J. Environ. Manage. 259. 109700. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109700.
Wu M., Liu J., Gao B., & Sillanpaa M. 2021. Phosphate substances transformation and vivianite formation in P-Fe containing sludge during the transition process of aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 319. 124259. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.124259.
Islam M.R., Bilkis S., Hoque T.S., Uddin S., Jahiruddin M., Rahman M.M., Siddique A.B., Hossain M.A., Danso Marfo T., Danish S., & Datta R. 2021. Mineralization of farm manures and slurries under aerobic and anaerobic conditions for subsequent release of phosphorus and sulphur in soil. Sustainability. 13(15). 8605. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/su13158605.
Sayara T., Basheer-Salimia R., Hawamde F., & Sánchez A. 2020. Recycling of organic wastes through composting: Process performance and compost application in agriculture. Agronomy. 10(11). 1838. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10111838.
Komiyama T., & Ito T. 2019. The characteristics of phosphorus in animal manure composts. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 65(3).281-288. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/00380768.2019.1615384.
Xie S., Tran H.T., Pu M., & Zhang T. 2023. Transformation characteristics of organic matter and phosphorus in composting processes of agricultural organic waste: Research trends. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 6. 331-342. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mset.2023.02.006.
Pattnaik S., Mohapatra B., & Gupta A. 2021. Plant growth-promoting microbe mediated uptake of essential nutrients (Fe, P, K) for crop stress management: Microbe–soil–plant continuum. Front. Agron. 3. 689972. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fagro.2021.689972.
Zhang T., Li H., Yan T., Shaheen S.M., Niu Y., Xie S., Zhang Y., Abdelrahman H., Ali E.F., Bolan N.S., & Rinklebe J. 2023. Organic matter stabilization and phosphorus activation during vegetable waste composting: Multivariate and multiscale investigation. Sci. Total Environ. 891.164608. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.164608.
Purba E.S.B. 2019. The effect of the duration of liquid organic fertilizer of tofu and lamtoro leaves with the addition of EM4 bioactivator on the total phosphorus and potassium content. Undergraduate Thesis. Yogyakarta: Universitas Sanata Dharma Yogyakarta.
Wang H., Xiao K., Yang J., Yu Z., Yu W., Xu Q., Wu Q., Liang S., Hu J., Hou H., & Liu B. 2020. Phosphorus recovery from the liquid phase of anaerobic digestate using biochar derived from iron− rich sludge: a potential phosphorus fertilizer. Water Res. 174. 115629. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.115629.
Oktrayadi O., Haitami A., & Ezward C. 2020. respon pemberian pupuk petroganik dan pupuk NPK phonska terhadap pertumbuhan dan produksi tanaman cabai merah (Capsicum Annum L.). Green Swarnadwipa: Jurnal Pengembangan Ilmu Pertanian. 9(2). 295-302.
Hanum C. 2013. Pertumbuhan, hasil, dan mutu biji kedelai dengan pemberian pupuk organik dan fosfor. J. Agron. Indonesia. 41(3). 209-214.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Indonesian Journal of Chemical Studies

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.