Hydraulics and Dynamics of Backwash in Filtration with Activated Carbon to Reduce Iron and Manganese in Groundwater
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55749/ss.v1i1.70Keywords:
Adsorption, Flow rate, Head loss, Reynolds number, Well water qualityAbstract
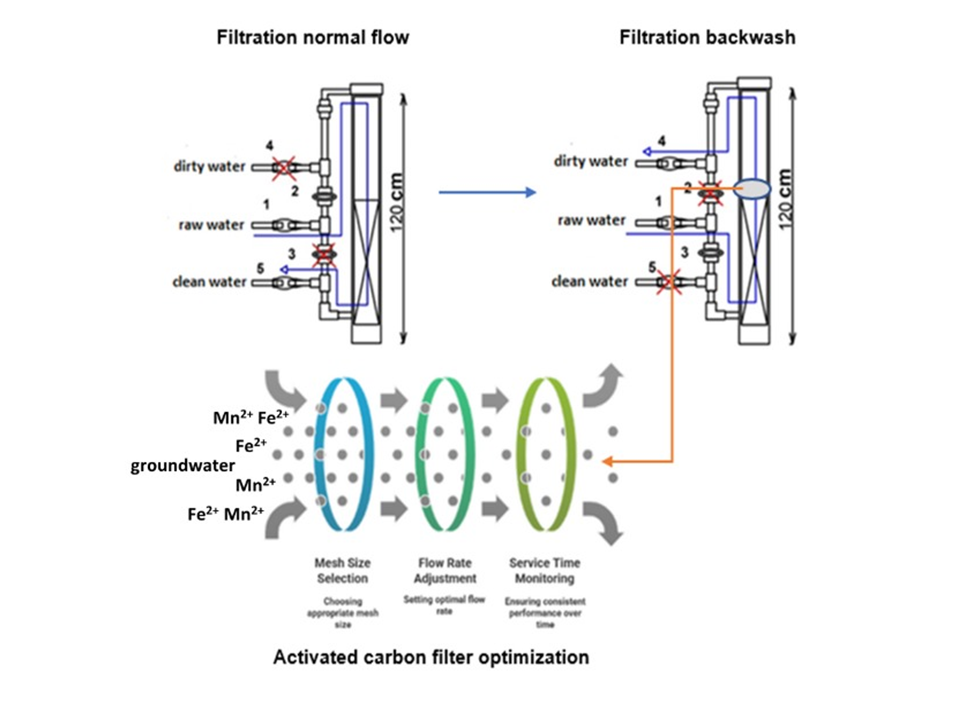
Well water used by the community often does not meet quality standards because it contains high levels of iron (Fe) and manganese (Mn). This study was intended to reduce Fe and Mn levels in well water by using filtration technique with activated charcoal media. The effect of hydraulics and backwash dynamics on the efficiency of filtration process was also investigated. The filtration apparatus was made of PVC pipe with the diameter of 4 inches and 120 cm height. The determination of optimum hydraulic conditions of filtration was carried out by varying the size of the activated carbon filter media (8-10, 12-14, and 16-18 mesh) and flow rate (1, 2, and 3 L/min) at the service time of 10 hours. The results showed that the size of filter media has significant effect on removal efficiency of Fe and Mn, with the most effective size was 16-18 mesh with the removal efficiency of 83.33% (Fe) and 93.33% (Mn). The highest head loss value in the filtration column was 0.15 cm, which occurred at the flow rate 3 L/min. Backwash should be performed after filtering process of 35 hours, 44 hours and 55 hours at the flow rate 1 L/min, 2 L/min, and 3 L/min repectively. The single filter design in this study reduced Fe and Mn concentration to meet clean water quality standards.
References
[1] Kurniawati, R.D., Kraar, M.H., Amalia, V.N., & Kusaeri, M.T. 2020. Peningkatan akses air bersih melalui sosialisasi dan penyaringan air sederhana desa haurpugur. J. Pengabdi. dan Peningkatan Mutu Masy. 1(2). 136–143. doi: https://doi.org/10.22219/janayu.v1i2.11784.
[2] Ghozali, A.A., Sohra, L.A., Eviane, D., Studi, P., Teknik, M., & Pascasarjana, S. 2023. efektivitas dan model isoterm adsorpsi Fe dan Mn oleh mata lele (Lemna minor) effectiveness and isotherm models of Fe and Mn Adsorption by Duckweeds (Lemna minor). J. Rekayasa Lingkung. 23(2). 11–21.
[3] Kristianingsih, Y., Masdianto, M., & Mardikawati, A. 2021. Penetapan kadar besi (Fe) dan mangan (Mn) pada air tanah pemukiman di sekitar setu pedongkelan Depok. Anakes J. Ilm. Anal. Kesehat. 7(2). 148–156. doi: https://doi.org/10.37012/anakes.v7i2.686.
[4] Elsheikh, M.A., Guirguis, H.S., & Fathy, A. 2016. A comparative study of methods used for Fe and Mn oxidation and removal from groundwater. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 63(4). 277–292.
[5] Thinojah, T. & Ketheesan, B. 2022. Iron removal from groundwater using granular activated carbon filters by oxidation coupled with the adsorption process. J. Water Clim. Chang. 13(5). 1985–1994. doi: https://doi.org/10.2166/wcc.2022.126.
[6] Qorina, R., Masthura, M., & Jumiati, E. 2023. Efektivitas penurunan Kadar Fe dan Mn pada air sumur gali kelurahan Jati Utomo Kota Binjai dengan metode filtrasi. J. Redoks. 8(2). 26–31. doi: https://doi.org/10.31851/redoks.v8i2.13155.
[7] Sunarto, S., Suyanta, S., Padmaningrum, R.T., Supiah YL, I., & Karlinda, K. 2022. Pemisahan ion logam besi dan mangan pada air sumur (dalam) wonoboyo menggunakan metode kolom adsorpsi. J. Sains Dasar. 11(1). 30–34. doi: https://doi.org/10.21831/jsd.v11i1.44189.
[8] Mangallo, B., Alfontus, R., & Novitasari, A.D. 2023. Efektifitas metode sand filter dalam menurunkan tingkat kekekruhan dan kadar e. coliform pada air sumur. J. Nat. 19(1). 1412–1328.
[9] Prayoga, Y.G. & Wulandari, W. 2024. Effectiveness of variations in silica sand and activated carbon filter media in reducing iron (Fe) levels in well water. Contag. Sci. Period. J. Public Heal. Coast. Heal. 6(1). 646. doi: https://doi.org/10.30829/contagion.v6i1.19816.
[10] Irawan, C. & Sunarno. 2019. Penyisihan Warna dan Kandungan Logam Fe, Mn dengan Proses Adsorpsi dan Filtrasi. Pros. SNRT (Seminar Nas. Ris. Ter.). 5662. 39–44.
[11] Wahyuni, A.S. 2019. Efektifitas filter carbon aktif dalam menurunkan kadar mangan (Mn) dan besi (Fe) dalam air tanah Puskesmas Kelapa Dua Kabupaten Tangerang. J. TechLINK. 3(1). 1–8.
[12] Zeng, X., Xia, J., Wang, Z., & Li, W. 2015. Removal of iron and manganese in steel industry drainage by biological activated carbon. Desalin. Water Treat. 56(9). 2543–2550. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2014.963682.
[13] Sri Widystuti & Antik Sepdian Sari. 2011. Kinerja pengolahan air bersih dengan proses filtrasi dalam mereduksi kesadahan. WAKTU: J. Tek. UNIPA. 9(1). 42–53.
[14] Stanojević, M. & Petković, A., 2024. Hidraulika pranja filtera sa aktivnim ugljem u postrojenjima za prečišćavanje vode. Zbornik Međunarodnog kongresa o procesnoj industriji–Procesing. 37(1). 99-107.
[15] Alkindi, H., Santosa, H., & Sutoyo, E. 2023. Analisis head losses pada circulating fluida air dalam dua jenis pipa. AME (Apl. Mek. dan Energi) J. Ilm. Tek. Mesin. 9(1). 51–56.
[16] Mwanat, M.H.M., Kasongo, K.B., Muliangala, F., Mwema, E., Makhatha, M.E., & Ngenda, R. 2024. Removal of Fe and Mn from Co leach solutions by adsorption on activated carbon based on post-consumer polyethylene terephthalate (PET)-mechanism insights through linear and nonlinear isotherm and kinetic models. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2024. 1–18. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2024.2315607.
[17] Kirchen, F., Fundneider, T., Gimmel, L., Thomann, M., Pulfer, M., & Lackner, S. 2024. Scattered and transmitted light as surrogates for activated carbon residual in advanced wastewater treatment processes: Investigating the influence of particle size. Water Res. X. 23. 100222. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wroa.2024.100222.
[18] Piche, A., Campbell, A., Cleary, S., Douglas, I., & Basu, O.D. 2019. Investigation of backwash strategy on headloss development and particle release in drinking water biofiltration. J. Water Process Eng. 32. 100895. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2019.100895.
[19] Sulianto, A.A., Kurniati, E., & Hapsari, A.A. 2019. Perancangan unit filtrasi untuk pengolahan limbah domestik menggunakan sistem downflow. J. Sumberd. Alam dan Lingkung. 6(3). 31–39. doi: https://doi.org/10.21776/ub.jsal.2019.006.03.4.
[20] Oktiawan, W. & Krisbiantoro. 2007. Efektifitas Penurunan Fe2+ dengan unit saringan pasir cepat media pasir aktif. J. Presipitasi Media Komun. dan Pengemb. Tek. Lingkungan. 2(1). 56–59.
[21] Schlichting, H. & Gersten, K. 2017. Boundary-Layer Theory, 9 th. Springer.
[22] Said, N.I. 2005. Metoda penghilangan zat besi dan mangan di dalam penyediaan air minum domestik. J. Air Indones. 1(3). 239–250. doi: https://doi.org/10.29122/jai.v1i3.2352.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Sorption Studies

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.









