Comparative Review of Metal Ferrites for Heavy Metals Adsorption in Water
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55749/ss.v1i2.132Keywords:
Adsorption, Heavy metal, Metal ferrites, Water treatment, MagneticAbstract
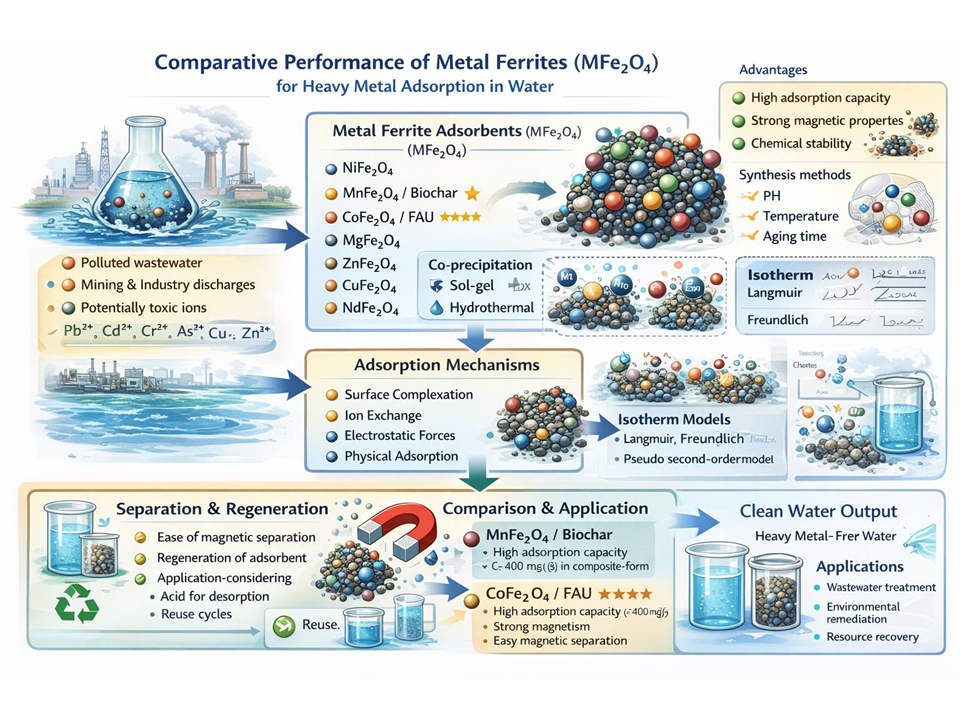
Heavy metal contamination in water is one of the most critical environmental issues, posing direct threats to human health and ecosystems. Various methods have been developed to address this problem; however, adsorption remains the most effective technique due to its simplicity, low cost, and regenerability. In this context, ferrite based materials (MFe2O4) offer great potential as heavy metal adsorbents owing to their combined advantages of magnetic properties, chemical stability, large surface area, and easy separation under an external magnetic field. This review paper provides a systematic comparison of various types of metal ferrites (Ni, Mn, Co, Zn, Mg, Cu, and Nd) applied for the removal of heavy metal ions from water. The comparison covers their crystal structures, morphology, surface area, magnetic properties, adsorption capacity, as well as the isotherm models and kinetics underlying the adsorption process. The findings show that each type of ferrite possesses specific advantages and limitations. NiFe2O4 exhibits high structural stability, MgFe2O4 demonstrates high adsorption capacity but is susceptible to dissolution under acidic conditions, CuFe2O4 exhibits strong chemical affinity, and NdFe2O4 shows potential selectivity toward specific ions. Meanwhile, MnFe2O4 and CoFe2O4, particularly in composite forms such as MnFe2O4/biochar and CoFe2O4/FAU, stand out with adsorption capacities exceeding 400 mg/g, sufficient magnetic properties, and easy magnetic separation, making them the most promising candidates for water treatment applications. This paper provides a comprehensive understanding of the structure property function relationship of metal ferrites as selective, stable, and efficient adsorbent materials for heavy metal remediation in aquatic environments.
References
[1] Sheel, V., Kotwal, A., Dumka, N., Sharma, V., Kumar, R., & Tyagi, V. 2024. Water as a social determinant of health: bringing policies into action. J. Glob. Health Rep. 8. e2024003. https://doi.org/10.29392/001c.92160
[2] Zhang, P., Yang, M., Lan, J., Huang, Y., Zhang, J., Huang, S., Yang, Y., & Ru, J. 2023. Water quality degradation due to heavy metal contamination: Health impacts and eco-friendly approaches for heavy metal remediation. Toxics. 11(10). 828. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics11100828
[3] Qasem, N.A.A., Mohammed, R.H. & Lawal, D.U. 2021. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater: a comprehensive and critical review. npj Clean Water. 4(1). 36. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-021-00127-0
[4] Yang, J., Huo, X., Li, Z., Li, H., Wang, T., & Ma, S. 2023. Study on adsorption and photocatalytic properties of zinc ferrite. Processes. 11(6). 1607. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11061607
[5] Nasirpouri, F., Fallah, S., Ahmadpour, G., Moslehifard, E., Samardak, A.Y., Samardak, V.Y., Ognev, A.V., & Samardak, A.S. 2023. Microstructure, ion adsorption and magnetic behavior of mesoporous γ-Fe₂O₃ ferrite nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 13. 25140–25158. https://doi.org/10.1039/D3RA01663C
[6] Qiao, J., Li, L., Liu, J ., Wu, N., Liu, W., Wu, F., & Zeng, Z. 2024. The vital application of rare earth for future high-performance materials: effects of RE doping on magnetic/spinel structures. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 176. 188-203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2023.09.003
[7] Iqbal, Z., Tanweer, M.S., & Alam, M. 2023. Reduced graphene oxide-modified spinel cobalt ferrite nanocomposite: synthesis, characterization, and its superior adsorption performance for dyes and heavy metals. ACS omega. 8(7). 6376-6390. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsomega.2c06636
[8] Andersen, H.L., Granados-Miralles, C., Jensen, K.M.Ø., Saura-Múzquiz, M., & Christensen. 2024. The chemistry of spinel ferrite nanoparticle nucleation, crystallization, and growth. ACS Nano. 18(14). 9852–9870. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.3c08772
[9] Phouthavong, V., Yan, R., Nijpanich, S., Hagio, T., Ichino, R., Kong, L., & Li, L. 2022. Magnetic adsorbents for wastewater treatment: advancements in their synthesis, properties and applications. Materials (Basel). 15(3). 1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031053
[10] Olawade, D.B., Wada, O.Z., Egbewole, B. I., Fapohunda, O., Ige, A.O., Usman, S.O., & Ajisafe, O. 2024. Metal and metal oxide nanomaterials for heavy metal remediation: mechanisms and performance. Front. Nanotechnol. 6. 1466721. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnano.2024.1466721
[11] El-Shater, R.E., Gasser, M. A., El-Kady, A. A., & El-Batal, F.H. 2023. Fabrication of doped ferrites and exploration of their structure and magnetic behavior. Mater. Adv. 4. 1234–1256. https://doi.org/10.1039/D3MA00105A
[12] Hassan, A.A., Fahim, Y.A. & Ali, M.E.M. 2025. Efficient removal of Cr(VI) and As(V) from aqueous solution using magnetically separable nickel ferrite nanoparticles. J. Clust. Sci. 36. 4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-024-02736-4
[13] Kumari, S., Sharma, R., Kondal, N., & Kumari, A. 2023. Alkaline earth metal doped nickel ferrites as a potential material for heavy metal removal from waste water. Mater. Chem. Phys. 301. 127582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2023.127582
[14] Lingamdinne, L.P., Kim, I.-S., Ha, J.-H., Chang, Y.-Y., Koduru, J. R., & Yang, J.-K. 2017. Enhanced adsorption removal of Pb(II) and Cr(III) by using nickel ferrite-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite. Metals 7(6). 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/met7060225
[15] Asadi, R., Abdollahi, H., Gharabaghi, M., & Boroumand, Z. 2020. Effective removal of Zn(II) ions from aqueous solution by the magnetic MnFe2O4 and CoFe2O4 spinel ferrite nanoparticles with focuses on synthesis, characterization, adsorption, and desorption. Adv. Powder Technol. 31(4). 1480-1489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2020.01.028
[16] Taguba, M.A.M., Ong, D.C., Ensano, B.M.B., Kan, C.-C., Grisdanurak, N., Yee, J.-J., & de Luna, M.D.G. 2021. Nonlinear isotherm and kinetic modeling of Cu(II) and Pb(II) uptake from water by MnFe2O4/Chitosan nanoadsorbents. Water. 13(12). 1662. https://doi.org/10.3390/w13121662
[17] Jung, K.W., Lee, S.Y., & Lee, Y.J. 2018. Facile one-pot hydrothermal synthesis of cubic spinel-type manganese ferrite/biochar composites for environmental remediation of heavy metals from aqueous solutions. Bioresour. Technol. 261. 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.04.003
[18] Shirkhodaie, M., Beyki, M. H., & Shemirani, F. 2016. Simple route synthesis of MnFe2O4@alunite composite for preconcentration of trace level of copper and lead from food and water samples. Desalin. Water Treat. 57(47). 22480-22492. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1130657
[19] Naz, S., Rasheed, T., Naqvi, S.T.R., Hussain, D., Fatima, B., ul Haq, M.N., Majeed, S., Shafi, S., Rizwan, K. and Ibrahim, M. 2020. Polyvinylpropyllidone decorated manganese ferrite based cues for the efficient removal of heavy metals ions from waste water. Physica B: Condens. Matter. 599. 412559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2020.41255
[20] Wang, J., Guan, M., Qin, Z., Zhang, S., Cheng, J., & Xin, B. 2025. Adsorption kinetics and isotherms of Cd(II), As(III), and Pb(II) on green Zn-Mn ferrite soft magnetic material. Water. 17(11). 1630. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17111630
[21] Amin, A.M., Rayan, D.A., Ahmed, Y.M., El-Shall, M.S., & Abdelbasir, S.M. 2022. Zinc ferrite nanoparticles from industrial waste for Se(IV) elimination from wastewater. J. Environ. Manage. 312. 114956. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.114956
[22] Tomina, E., Novikova, L., Kotova, A., Meshcheryakova, A., Krupskaya, V., Morozov, I., Koroleva, T., Tyupina, E., Perov, N. and Alekhina, Y. 2023. ZnFe2O4/zeolite nanocomposites for sorption extraction of Cu2+ from aqueous medium. AppliedChem. 3(4). 452-476. https://doi.org/10.3390/appliedchem3040029
[23] Allwin Mabes Raj, A.F.P., Bauman, M., Dimitrušev, N., Ali, L.M. A., Onofre, M., Gary-Bobo, M., Durand, J.-O., Lobnik, A., & Košak, A. 2023. Superparamagnetic spinel-Ferrite nano-adsorbents Adapted for Hg2+, Dy3+, Tb3+ removal/recycling: synthesis, characterization, and assessment of toxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24(12). 10072. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms241210072
[24] Paris, E.C., Malafatti, J.O., Musetti, H.C., Manzoli, A., Zenatti, A., & Escote, M.T. 2020. Faujasite zeolite decorated with cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for improving removal and reuse in Pb2+ ions adsorption. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 28(7). 1884-1890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjche.2020.04.019
[25] Tran, Q.A., Tran, N.L., Anh, D.K.N., Thi, Q.N.L., Nguyen, T.L., Nguyen, H.T.P., Nguyen, A.T., Nguyen, Q.T., & Le, T.K. 2022. Synthesis of magnetic chromium substituted cobalt ferrite Co(CrxFe1-x)2O4 adsorbents for phosphate removal. Condens. Matter Ph. 24(3). 306-314. https://doi.org/10.17308/kcmf.2022.24/9852
[26] Tatarchuk, T., Shyichuk, A., Sojka, Z., Gryboś, J., Naushad, M., Kotsyubynsky, V., Kowalska, M., Kwiatkowska-Marks, S. and Danyliuk, N. 2021. Green synthesis, structure, cations distribution and bonding characteristics of superparamagnetic cobalt-zinc ferrites nanoparticles for Pb(II) adsorption and magnetic hyperthermia applications. J. Mol. Liq. 328. 115375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.115375
[27] Ramadan, R., & Shafaay, A.S. 2023. Efficient lead removal from aquatic solution by (Co0.7Zn0.3)0.9Ni0.1Fe2O4 ferrite with tunable optical and magnetic properties. J. Water Process Eng. 54. 103958. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2023.103958
[28] Mahmud, M., Sahadat Hossain, Md., Bin Mobarak, M., Sultana, S., Sharmin, S., & Ahmed, S. 2022. Co-precipitation synthesis of non-cytotoxic and magnetic cobalt ferrite nanoparticles for purging heavy metal from the aqueous medium: Pb(II) adsorption isotherms and kinetics study. Chem. Ecol. 38(6). 544–563. https://doi.org/10.1080/02757540.2022.2093351
[29] Sahare, S.P., & Zodape, S.P. 2025. Removal of Cu(II) and Cd(II) ions from aqueous solutions by methionine functionalized cobalt-magnesium ferrite chitosan beads: performance and adsorption mechanism. J. Polym. Environ. 31. 1967–1985. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-022-02724-7
[30] Uddin, M.J., & Jeong, Y.K. 2022. Application of magnesium ferrite nanomaterials for adsorptive removal of arsenic from water: Effects of Mg and Fe ratio. Chemosphere. 307. 135817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135817
[31] Irfan, M., Zaheer, F., Hussain, H., Naz, M.Y., Shukrullah, S., Legutko, S., Mahnashi, M.H., Alsaiari, M.A., Ghanim, A.A.J., Rahman, S. and Alshorman, O. 2022. Kinetics and adsorption isotherms of amine-functionalized magnesium ferrite produced using sol-gel method for treatment of heavy metals in wastewater. Materials. 15(11). 4009. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15114009
[32] Tatarchuk, T., Myslin, M., Lapchuk, I., Shyichuk, A., Murthy, A.P., Gargula, R., Kurzydło, P., Bogacz, B.F. and Pędziwiatr, A.T., 2021. Magnesium-zinc ferrites as magnetic adsorbents for Cr(VI) and Ni(II) ions removal: Cation distribution and antistructure modeling. Chemosphere. 270. 129414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129414
[33] Kurup, G., Krishnan, N., R, V.M., R, R.A., Nithya, K., Sathish, A., Sivamani, S. and Cheruvally, A.S. 2024. Competitive adsorption studies of MgFe2O4-Biochar nanocomposites for the removal of chromium and nickel ions in single and binary metal ion system. Adsorption. 30(7). 1805-1827. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-024-00523-1
[34] Meirelles, M.R., Malafatti, J.O.D., Escote, M.T., Pinto, A.H., & Paris, E.C. 2023. Magnetic adsorbent based on faujasite zeolite decorated with magnesium ferrite nanoparticles for metal ion removal. Magnetochemistry. 9(5). 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry9050136
[35] Tran, C.V., Quang, D.V., Nguyen Thi, H.P., Truong, T.N., & La, D.D. 2020. Effective removal of Pb(II) from aqueous media by a new design of Cu–Mg binary ferrite. ACS Omega. 5(13). 7298-7306. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b04126
[36] Song, X., Xu, C., Yao, W., Wen, J., Wei, Q., Li, Y., & Feng, X. 2023. Study on the controllable preparation of Nd3+ doped in Fe3O4 nanoparticles for magnetic protective fabrics. Molecules. 28(7). 3175. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28073175
[37] Abidin, M.Z.U., Ikram, M., Moeen, S.S., Nazir, G., Kanoun, M. B., & Goumri-Said, S. 2024. A comprehensive review on the synthesis of ferrite nanomaterials via bottom-up and top-down approaches: advantages, disadvantages, characterization and computational insights. Coord. Chem. Rev. 520. 216158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2024.216158
[38] Yao, B., Luo, Z., Du, S., Yang, J., Zhi, D., & Zhou, Y. 2022. Magnetic MgFe₂O₄/biochar derived from pomelo peel as a persulfate activator for levofloxacin degradation: effects and mechanistic consideration. Bioresour. Technol. 346. 126547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126547
[39] Dippong, T., Cadar, O., & Levei, E.A. 2022). Effect of transition metal doping on the structural, morphological, and magnetic properties of NiFe₂O₄. Materials. 15(9).2996. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15092996
[40] Azzam, A.B., Tokhy, Y. A., Dars, F. M. E., & Younes, A. A. 2023. Heterogeneous porous biochar-supported nano NiFe2O4 for efficient removal of hazardous antibiotic from pharmaceutical wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30(56). 119473-119490. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-30587-5
[41] Khalaj, M., Khatami, S.M., Kalhor, M., Zarandi, M., Anthony, E. T., & Klein, A. 2023. Polyethylenimine grafted onto nano-NiFe2O4@SiO2 for the removal of CrO42−, Ni2+, and Pb2+ ions from aqueous solutions. Molecules. 29(1). 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29010125
[42] Kadhi, N.S., Senani, G.M., Saad, F.A., Munshi, A. M., & Abdelrahman, E.A. 2024. Modification of nickel ferrite nanoparticles by sodium docusate surfactant for superior crystal violet dye removal from aqueous solutions. Sci. Rep. 14. 27973. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-77608-y
[43] Altaf, M., Ishaq, M., Yousaf, T., & Hussain, A.A. 2024. Experimental overview of nanoferrites: synthesis, characterization and performance evaluation in wastewater treatment. Mater. Res. Express. 11. 105005. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ad82ab
[44] Salih, S. J. & Mahmood, W. M. (2023). Review On Magnetic spinel ferrite (MFe₂O₄) nanoparticles: from synthesis to application. Heliyon. 9. e 16601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16601
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Sorption Studies

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.









