Recent Advances in Nickel Ferrite-Polymer Nanocomposites for Radar Absorbing Material Applications
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.55749/ss.v1i2.125Keywords:
Composites, Nickel ferrite, Polymer, Radar absorbing materialAbstract
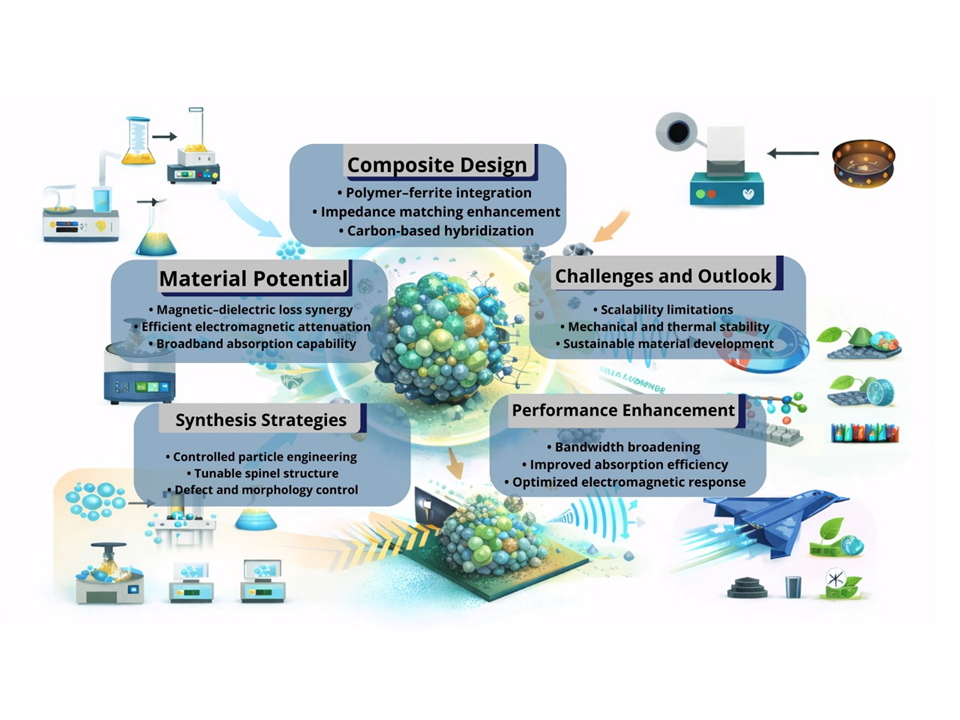
Nickel ferrite (NiFe₂O₄) and its polymer-based composites have emerged as promising candidates for radar absorbing materials (RAMs) due to their unique combination of magnetic and dielectric loss mechanisms. This review highlights recent advances in synthesis strategies, including sol–gel, hydrothermal, co-precipitation, and microwave-assisted methods, which enable precise control of particle size, morphology, and crystallographic defects. Such control supports flexible structural design of nickel ferrite spinel structures, allowing dopant incorporation to tailor magnetic anisotropy and saturation magnetization. These structural features directly affect electromagnetic performance. Magnetic loss is mainly governed by natural resonance and, to a lesser extent, eddy current effects, while dielectric loss arises from dipole polarization, interfacial polarization, and conduction loss. The synergistic balance of magnetic and dielectric losses makes nickel ferrite–polymer nanocomposites promising broadband radar absorbing materials. The discussion emphasizes the role of cation substitution, polymer matrices, and hybridization with carbon-based materials in enhancing microwave absorption bandwidth and impedance matching. Various synthesis approaches, including sol–gel, hydrothermal, and in-situ polymerization, are compared with respect to their influence on particle size, morphology, and absorption efficiency. Challenges such as limited bandwidth, thermal and mechanical stability, and scalability are highlighted, along with potential solutions through advanced nanostructuring, multifunctional design, and sustainable synthesis. Future research directions are also outlined to support the development of next-generation stealth and electromagnetic interference shielding technologies.
References
[1] Houbi, A., Aldashevich, Z.A., Atassi, Y., Telmanovna, Z.B., Saule, M. and Kubanych, K. 2021. Microwave absorbing properties of ferrites and their composites: A review. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 529. 167839. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2021.167839
[2] Rybicki, T., Stempien, Z. and Karbownik, I. 2021. EMI Shielding and absorption of electroconductive textiles with PANI and PPy conductive polymers and numerical model approach. Energies. 14(22). 7746. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14227746
[3] Imran Din, M., Rafique, F., Hussain, M.S., Arslan Mehmood, H. and Waseem, S., 2019. Recent developments in the synthesis and stability of metal ferrite nanoparticles. Sci. Prog. 102(1). 61–72. https://doi.org/10.1177/0036850419826799
[4] Salih, S.J. and Mahmood, W.M. 2023. Review on magnetic spinel ferrite (MFe2O4) nanoparticles: from synthesis to application. Heliyon. 9(6). e16601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16601
[5] Prekodravac Filipovic, J., Milenkovic, M., Kepic, D., Dorontic, S., Yasir, M., Nardin, B. and Jovanovic, S., 2025. Electromagnetic interference in the modern era: concerns, trends, and nanomaterial-based solutions. Nanomaterials. 15(20). 1558. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano15201558
[6] Abubakar, I., Din, J., Alhilali, M. and Lam, H.Y., 2017. Interference and electromagnetic compatibility challenges in 5G wireless network deployments. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 5(3). 612-621. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijeecs.v5.i3.pp612-621
[7] Yustanti, E., Noviyanto, A., Chotimah, L.C., Saputra, M.A.R., Randa, M. and Manawan, M. 2022. Increased electromagnetic wave absorption through controlled sonication processing on BaFe11.2Mg0.4Al0.4O19 nanoparticles. Coatings. 12(9). 1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12091367
[8] Hwata, C., Rushingabigwi, G., Gatera, O., Mukalinyigira, D., Twizere, C., Thomas, B.N. and Peluffo-Ord’onez, D.H. 2025. Internet of things-based electromagnetic compatibility monitoring (IEMCM) architecture for biomedical devices. Appl. Sci. 15(22). 12337. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212337
[9] Yucheng, L. and Yubin, L. 2010. Design strategy of anti-electromagnetic interference for microcomputer relay protection system. In 2010 International Forum on Information Technology and Applications. 2. 180-183. https://doi.org/10.1109/IFITA.2010.78
[10] Barmore, W., Patel, H., Voong, C., Tarallo, C. and Calkins Jr, J.B. 2022. Effects of medically generated electromagnetic interference from medical devices on cardiac implantable electronic devices: A review. World J. Cardiol. 14(8). 446–453. https://doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v14.i8.446
[11] Perez, R. 2023. Analyzing fault propagation and designing fault containment for aerospace. In 2023 IEEE Aerospace Conference. 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1109/AERO55745.2023.10115842
[12] Pavlík, M., Bereš, M. and Beňa, Ľ. 2024. The influence of various commonly used building materials on the shielding effectiveness, reflection and absorption of the electromagnetic wave. Appl. Sci. 14(6). 2521. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14062521
[13] Kumar, S., Kumar, B., Sehgal, R., Wani, M.F., Kumar, D., Sharma, M.D., Singh, V., Sehgal, R. and Kumar, V. 2023. Advantages and disadvantages of metal nanoparticles. In Nanoparticles reinforced metal nanocomposites: mechanical performance and durability (pp. 209-235). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-9729-7_7
[14] Cheng, J., Li, C., Xiong, Y., Zhang, H., Raza, H., Ullah, S., Wu, J., Zheng, G., Cao, Q., Zhang, D. and Zheng, Q. 2022. Recent advances in design strategies and multifunctionality of flexible electromagnetic interference shielding materials. Nano-Micro Lett. 14(1). 80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40820-022-00823-7
[15] Sambhudevan, S., 2021. Ferrite-based polymer nanocomposites as shielding materials: a review. Chem. Pap. 75(8). 3697-3710. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-021-01664-1
[16] Gheisari, K., Javadpour, S., Shokrollahi, H. and Hashemi, B., 2008. Magnetic losses of the soft magnetic composites consisting of iron and Ni–Zn ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320(8). 1544-1548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2008.01.005
[17] Al-Saleh, M.H., Saadeh, W.H. and Sundararaj, U., 2013. EMI shielding effectiveness of carbon based nanostructured polymeric materials: a comparative study. Carbon. 60. 146-156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2013.04.008
[18] Aritonang, S., Hijrianisa, A., Pratita, E., Ningrum, H.S. and Pangestu, B.B. 2024. Drone berbahan komposit serat rami dengan karbon aktif-barium m-heksaferit sebagai radar absorbing material. Jurnal Rekayasa Material, Manufaktur dan Energi. 7(1). 35-43. https://doi.org/10.30596/rmme.v7i1.17283
[19] Kim, S.H., Lee, S.Y., Zhang, Y., Park, S.J. and Gu, J. 2023. Carbon‐based radar absorbing materials toward stealth technologies. Adv. Sci. 10(32). 2303104. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202303104
[20] Kostishin, V.G., Isaev, I.M. and Salogub, D.V. 2024. Radio-absorbing magnetic polymer composites based on spinel ferrites: a review. Polymers. 16(7). 1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16071003
[21] Khedr, M.H., Omar, A.A. and Abdel-Moaty, S.A. 2006. Magnetic nanocomposites: preparation and characterization of Co-ferrite nanoparticles. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 281(1–3). 8–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2006.02.005
[22] Nha, T.T.N., Prakash, S.H., Roopan, S.M., Samuel, J.J., Toan, D.N., Khan, D.T., Bich, D.D., Thanh, T.D., Ngan, L.T.T., Manh, D.H. and Phong, P.T. 2025. Microwave-assisted co-precipitation synthesis of MFe2O4 nanoferrites (M= Co and Mn) using biogenic coir extract and their physical characterization. RSC Adv. 15(36). 29571-29592. https://doi.org/10.1039/D5RA04897D
[23] Malere, C.P., Donati, B., Eras, N., Silva, V.A. and Lona, L.F. 2022. Electromagnetic evaluation of radar absorbing materials based on conducting polypyrrole and organic–inorganic nanocomposite of polypyrrole/kaolinite. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 139(17). 52023. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.52023
[24] Dubey, V. and Kain, V. 2018. Synthesis of magnetite by coprecipitation and sintering and its characterization. Mater. Manuf. Process. 33(8). 835-839. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2017.1401720
[25] Dudhal, R.D., Patade, S., Andhare, D., Paralikar, R., Chilwar, R. and More, S.D. 2020. Influence of fuel to metal nitrate ratio on the structural properties of nickel ferrite. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1644(1). 012011. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1644/1/012011
[26] Abd-Elkader, O.H., Deraz, N.M. and Aleya, L. 2023. Effects of zinc substitution on the microstructural and magnetic characteristics of cubic symmetry nickel ferrite system. Symmetry. 15(5). 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym15050975
[27] Li, J., Zhou, D., Wang, P.J., Du, C., Liu, W.F., Su, J.Z., Pang, L.X., Cao, M.S. and Kong, L.B. 2021. Recent progress in two-dimensional materials for microwave absorption applications. Chem. Eng. J. 425. 131558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.131558
[28] Kavitha, S. and Kurian, M. 2019. Effect of zirconium doping in the microstructure, magnetic and dielectric properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 799. 147-159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.05.183
[29] Habibi, M.H. and Fakhri, F. 2017. Low temperature preparation, characterization, magnetic measurements, thermal, optical, morphological and photo-catalytic properties of nano-size single phase nickel ferrite NiFe2O4. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28(18). 13455-13463. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7184-z
[30] Aggarwal, N. and Narang, S.B. 2020. X-band microwave analysis and characterization of zinc substituted nickel ferrites prepared by sol–gel citrate route. J. Electron. Mater. 49(1). 668-680. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-019-07694-6
[31] Narang, S.B. and Pubby, K. 2021. Nickel spinel ferrites: a review. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 519. 167163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2020.167163
[32] Isasi, J., Arévalo, P., Martin, E. and Martín-Hernández, F. 2019. Preparation and study of silica and APTES–silica-modified NiFe2O4 nanocomposites for removal of Cu2+ and Zn2+ ions from aqueous solutions. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 91(3). 596-610. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-019-05067-3
[33] Sagadevan, S., Chowdhury, Z.Z. and Rafique, R.F. 2018. Preparation and characterization of nickel ferrite nanoparticles via co-precipitation method. Mater. Res. 21(2). e20160533. https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5373-mr-2016-0533
[34] Ismail, I. and Azis, R.A.S. 2024. A review of magnetic nanocomposites for EMI shielding: synthesis, properties, and mechanisms. J. Mater. Sci. 59(13). 5293-5329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-024-09527-2
[35] Bokov, D., Turki Jalil, A., Chupradit, S., Suksatan, W., Javed Ansari, M., Shewael, I.H., Valiev, G.H. and Kianfar, E. 2021. Nanomaterial by sol‐gel method: synthesis and application. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021(1). 5102014. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/5102014
[36] Yue, X., Fan, J. and Xiang, Q. 2022. Internal electric field on steering charge migration: modulations, determinations and energy‐related applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32(12). 2110258. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202110258
[37] Samet, M., Kallel, A. and Serghei, A. 2022. Maxwell-Wagner-Sillars interfacial polarization in dielectric spectra of composite materials: Scaling laws and applications. J. Compos. Mater. 56(20). 3197-3217. https://doi.org/10.1177/00219983221090629
[38] Khoreem, S.H. and Al-Hammadi, A.H. 2025. Tailoring the functional properties of BaNi₂₋ₓZnₓFe₁₆O₂₇ ferrites via ceramic route for advanced electronic and energy applications. Discov. Mater. 5(1). 173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43939-025-00374-9
[39] Gómez, C.A.P., McCoy, J.J., Weber, M.H. and Lynn, K.G. 2019. Effect of Zn for Ni substitution on the properties of Nickel-Zinc ferrites as studied by low-energy implanted positrons. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 481. 93-99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.03.002
[40] Borge-Duran, I., Paul, A. and Grinberg, I. 2023. From Non-Magnetic to Magnetic: A First-Principles Study of the Emergence of Magnetism in 2D (Nb1–xTix) 4C3 MXenes. Chem. Mater. 35(18). 7442-7449. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.3c00367
[41] Zhou, W., Cao, G., Yuan, M., Zhong, S., Wang, Y., Liu, X., Cao, D., Peng, W., Liu, J., Wang, G. and Dang, Z.M. 2023. Core–shell engineering of conductive fillers toward enhanced dielectric properties: a universal polarization mechanism in polymer conductor composites. Adv. Mater. 35(2). 2207829. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202207829
[42] Moučka, R., Sedlačík, M., Prokeš, J., Kasparyan, H., Valtera, S. and Kopecký, D. 2020. Electromagnetic interference shielding of polypyrrole nanostructures. Synth. Met. 269. 116573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synthmet.2020.116573
[43] Aytaç, A., İpek, H., Aztekin, K., Aytav, E. and Çanakçı, B. 2020. A review of the radar absorber material and structures. Sci. J. Mil. Univ. L. Forces. 198(4). 931–946. https://doi.org/10.5604/01.3001.0014.6064
[44] Sulaiman, J.M. and Calinescu, I. 2022. Electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding and microwave absorption properties of nickel ferrite NiFe2O4/PANI-PTSA nanocomposite. Adv. Mater. Process. Technol. 8(2). 1312-1323. https://doi.org/10.1080/2374068X.2020.1856635
[45] Manobalan, S., Mahender, C., Rajan Babu, D., Rahaman, A., Sreekanth, M.S., Sharma, D., Bose, S. and Sumangala, T.P. 2022. The mechanical, dielectric, and EMI shielding properties of nickel ferrite (NiF)/graphene (Gr)-doped epoxy composites. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 32(10). 4077-4091. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-022-02419-5
[46] Mansha, A., Zubair, K., Rehan, Z.A., Shakir, H.F., Javed, T., Shabbir, R., Mustafa, S.K., Mora-Poblete, F., Zhou, J.R., Kumar, U. and Al-Harbi, M.S. 2021. Synthesis of nickel spinel ferrites nanoparticles coated with thermally reduced graphene oxide for EMI shielding in the microwave, UV, and NIR regions. Polymers. 13(19). 3316. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13193316
[47] Meaz, T.M., Saafan, S.A., El-Ghazzawy, E.H., Ayad, M.M. and El Nimr, M.K. 2012. Comparative study of dielectric properties of (Ni Zn ferrite nanoparticles/polypyrrole) composites with different PPy percentages. J. Am. Sci. 8(8). 1035-1041.
[48] Saini, M., Shukla, R. and Kumar, A. 2019. Cd2+ substituted nickel ferrite doped polyaniline nanocomposites as effective shield against electromagnetic radiation in X-band frequency. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 491. 165549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2019.165549
[49] Kostishyn, V.G., Isaev, I.M., Shakirzyanov, R.I., Salogub, D.V., Kayumova, A.R. and Olitsky, V.K. 2023. Radar absorbing properties of polyvinyl alcohol/Ni–Zn ferrite-spinel composite. Tech. Phys. 68(2). S178-S184. https://doi.org/10.21883/tp.2022.01.52540.217-21
[50] Zhao, H., Sun, X., Mao, C. and Du, J. 2009. Preparation and microwave–absorbing properties of NiFe2O4-polystyrene composites. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 404(1). 69-72., https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2008.10.006
[51] Sulistiyo, H., Farhan, M.F., Soraya, N.A. and Gunadi, G.I. 2022. Material lapisan anti-radar untuk menyamarkan kawasan strategis dan sarana pendukung militer (markas TNI, hanggar pesawat tempur, hanggar tank dan gudang amunisi). J. Kewarganegaraan. 6(4). 6642-6649. https://doi.org/10.31316/jk.v6i4.4223
[52] Thomas, P., Abdulhakim, L.V., Pushkaran, N.K. and Karuvandi, A.C. 2020. Wideband radar absorbing structure using polyaniline-graphene nanocomposite. C. 6(4). 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/c6040072
[53] Zong, M., Huang, Y., Ding, X., Zhang, N., Qu, C. and Wang, Y. 2014. One-step hydrothermal synthesis and microwave electromagnetic properties of RGO/NiFe2O4 composite. Ceram. Int. 40(5). 6821-6828. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2013.11.145
[54] Iranmanesh, P., Yazdi, S.T., Mehran, M. and Saeednia, S. 2018. Superior magnetic properties of Ni ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by capping agent-free one-step coprecipitation route at different pH values. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 449. 172-179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.10.040
[55] Jahanbin, T., Hashim, M. and Mantori, K.A. 2010. Comparative studies on the structure and electromagnetic properties of Ni− Zn ferrites prepared via co-precipitation and conventional ceramic processing routes. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322(18). 2684-2689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2010.04.008
[56] Chan, Y.L., You, K.Y., Mayzan, M.Z.H., Jusoh, M.A., Abbas, Z. and Esa, F. 2020. Investigation into return loss characteristic of graphene oxide/zinc ferrite/epoxy composite at X-band frequency. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. 23(4). 593-602. https://doi.org/10.6180/jase.202012_23(4).0003
[57] Hou, T., Jia, Z., Wang, B., Li, H., Liu, X., Bi, L. and Wu, G. 2021. MXene-based accordion 2D hybrid structure with Co9S8/C/Ti3C2Tx as efficient electromagnetic wave absorber. Chem. Eng. J. 414. 128875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.128875
[58] Li, J., Zhou, D., Wang, P.J., Du, C., Liu, W.F., Su, J.Z., Pang, L.X., Cao, M.S. and Kong, L.B. 2021. Recent progress in two-dimensional materials for microwave absorption applications. Chem. Eng. J. 425. 131558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.131558
[59] Gu, Q., Jafarian, M., Afghahi, S.S.S., Atassi, Y. and Al-Qassar, R. 2020. Tuning the impedance matching characteristics of microwave absorbing paint in X-band using copper particles and polypyrrole coating. Mater. Res. Bull. 125. https://doi.org/110780. 10.1016/j.materresbull.2020.110780
[60] Planes, E., Gloaguen, F. and Flandin, L. 2015. Optimizing formulations of polymer composite with high filler content: Application to bipolar plate. Compos. Sci. Technol. 110. 17-25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2015.01.009
[61] Xu, Z., Li, J., Li, J., Du, J., Li, T., Zeng, W., Qiu, J. and Meng, F. 2023. Bionic structures for optimizing the design of stealth materials. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 25(8). 5913-5925. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP06086H
[62] Gill, N., Sharma, A.L., Gupta, V., Tomar, M., Pandey, O.P. and Singh, D.P. 2019. Enhanced microwave absorption and suppressed reflection of polypyrrole-cobalt ferrite-graphene nanocomposite in X-band. J. Alloys Compd. 797. 1190-1197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.05.176
[63] Zhu, W., Wang, L., Zhao, R., Ren, J., Lu, G. and Wang, Y. 2011. Electromagnetic and microwave-absorbing properties of magnetic nickel ferrite nanocrystals. Nanoscale. 3(7). 2862-2864. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1nr10274e
[64] Kartika, D.M., Rusmana, A. and Sumpena, P. 2021. Structural, magnetic, and X-band microwave absorbing properties of Ni-ferrites prepared using oxidized mill scales. J. Elektron. Telekomun. 21(1). 27-34. https://doi.org/10.14203/jet.v21.27-34
[65] Yunas, Y., Adi, W.A., Mashadi, M. and Rahmy, P.A. 2017. Magnetic and microwave absorption properties of nickel ferrite (NixFe3-xO4) by HEM technique. Malaysian J. Fundam. Appl. Sci. 13(3). 203–206. https://doi.org/10.11113/mjfas.v13n3.553
[66] Guo, L., He, Y., Chen, D., Du, B., Cao, W., Lv, Y. and Ding, Z., 2021. Hydrothermal synthesis and microwave absorption properties of nickel ferrite/multiwalled carbon nanotubes composites. Coatings. 11(5). 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11050534
[67] Harris, V.G. 2011. Modern microwave ferrites. IEEE Trans. Magn. 48(3). 1075-1104. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2011.2180732
[68] Somboonsub, B., Srisuwan, S., Invernale, M.A., Thongyai, S., Praserthdam, P., Scola, D.A. and Sotzing, G.A., 2010. Comparison of the thermally stable conducting polymers PEDOT, PANi, and PPy using sulfonated poly (imide) templates. Polymer. 51(20). 4472-4476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2010.08.008
[69] Subudhi, P. and Punetha, D., 2023. Progress, challenges, and perspectives on polymer substrates for emerging flexible solar cells: A holistic panoramic review. Prog. Photovoltaics Res. Appl. 31(8). 753-789. https://doi.org/10.1002/pip.3703
[70] Darr, J.A., Zhang, J., Makwana, N.M. and Weng, X., 2017. Continuous hydrothermal synthesis of inorganic nanoparticles: applications and future directions. Chem. Rev. 117(17). 11125-11238. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00417
[71] Koul, S.K., Praveen, M. and Karthikeya, G.S. 2025. Microwave absorbers: materials engineering. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-96-9596-6_6
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Sorption Studies

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.









